| Length: 25 inches | Wingspan: 58 inches | Seasonality: Non-resident in South Dakota |
| ID Keys: Yellow legs, large yellow bill, gray wings with black and white contrasting tips, white body and head | ||
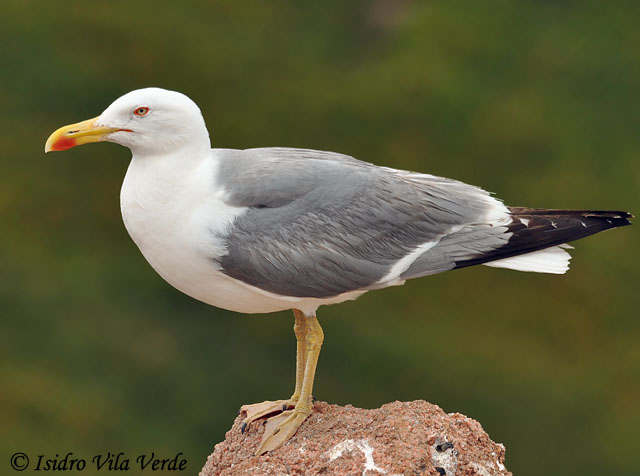 The
Yellow-legged Gull is very similar to the
Herring Gull, and was once considered a race of the Herring Gull
species. The yellow legs separate the Yellow-legged Gull from the
pink-legged Herring Gull, as do slight differences in mantle color and
wingtip patterns. The mantle color of a Yellow-legged Gull is lighter
than the similar Lesser
Black-backed Gull. There was significant confusion about the
species' status in North America, as some North American sightings of what
were undoubtedly Yellow-legged Gulls were assumed to be hybrid Herring and
Lesser Black-backed Gulls, a cross which has been confirmed.
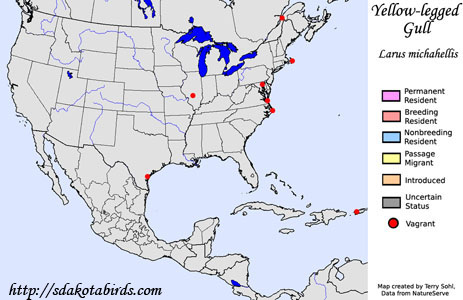
Yellow-legged Gulls are natives of southern Europe, northern Africa, and the
Middle East, and are but rare visitors to North America, with most sightings
occurring in the northeastern part of the United States.
The
Yellow-legged Gull is very similar to the
Herring Gull, and was once considered a race of the Herring Gull
species. The yellow legs separate the Yellow-legged Gull from the
pink-legged Herring Gull, as do slight differences in mantle color and
wingtip patterns. The mantle color of a Yellow-legged Gull is lighter
than the similar Lesser
Black-backed Gull. There was significant confusion about the
species' status in North America, as some North American sightings of what
were undoubtedly Yellow-legged Gulls were assumed to be hybrid Herring and
Lesser Black-backed Gulls, a cross which has been confirmed.
Yellow-legged Gulls are natives of southern Europe, northern Africa, and the
Middle East, and are but rare visitors to North America, with most sightings
occurring in the northeastern part of the United States.
Habitat: Found in a variety of habitats both during and outside of the breeding season. When breeding, colonies may occur on rocky shorelines, on offshore islands, near freshwater wetlands and water bodies, or brackish marshes. Outside of the breeding season, they are found near a wide variety of aquatic habitats.
Diet: Omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food items, including fish, crustaceans, mollusks, insects, small vertebrates, eggs and young birds, carrion, and refuse.
Behavior: Gregarious in all seasons, nesting in colonies, and typically found in groups outside of the breeding season as well. Foraging method depends upon location and food item being pursued. They have adapted well to a human presence, and can often be found at garbage dumps or in other areas where human refuse is available.
Nesting: Yellow-legged Gulls are colonial nesters. The nest is a mound of vegetation, feathers, and other material, depressed in the center, and placed on the ground, in a rocky crevice, on a cliff ledge, or even on man-made structures such as buildings. The female usually lays 3 eggs. The young fledge after about 5 weeks.
Song: The common call of a Yellow-legged Gull is a rough low kaw.
Migration: Many birds are permanent residents in their normal European and African range. However, some birds move to more temperate climates for the winter, departing for southwestern Europe or North Africa.
Interactive eBird map: Click here to access an interactive eBird map of Yellow-legged Gull sightings
Similar Species: Very similar to the Lesser Black-backed Gull, Herring Gull.
Conservation Status: Populations are large, they appear to be increasing, and they are spread over a wide geographic area. The IUCN lists the Yellow-legged Gull as a species of "Least Concern".
Further Information: 1) Royal Society for the Protection of Birds - Yellow-legged Gull
2) BirdLife International - Yellow-legged Gull
3) Yellow-legged Gulls in North America
Photo Information: Photo taken by Isidro Vila Verde - July 3rd, 2010 - Portugal - Photo licensed under Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 2.0 Generic License.
| Click below for a higher-resolution map |
 |
| South Dakota Status: Non-resident in South Dakota |
Additional Yellow-legged Gull Photos (coming soon!!)
